Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
November 2022
10 AWS security considerations when migrating
Cloud data storage has many practical advantages over traditional data centers, but making a move also comes with many unique security considerations. When moving to AWS, begin how you wish to continue. Companies that transition to cloud data storage must update their approach to information security to protect their data. Setting up proper security practices during migration will help future teams securely and efficiently deliver applications and features.
How to Migrate Snyk to the new Bitbucket Cloud App Integration
OT:ICEFALL Continues: Vedere Labs Discloses Three New Vulnerabilities Affecting OT Products - How to Mitigate
Continuing our OT:ICEFALL research, Vedere Labs has disclosed three new vulnerabilities affecting OT products from two German vendors: Festo automation controllers and the CODESYS runtime, which is used by hundreds of device manufacturers in different industrial sectors, including Festo.
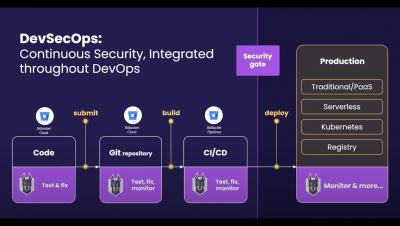
Can gamification unite development and security?
Despite years of effort encouraging a DevSecOps approach, development and security teams tend to remain divided. For example, according to 2020 research, 65% of security professionals reported that their companies had successfully shifted security left. Good, right? But the same research also shows that almost a third of people believe the security team is primarily responsible for security — despite shifting left.
Omdia On the Radar: Cyberpion offers a platform to reduce external attack surfaces
Cybersecurity solutions from ManageEngine
2022 Kubernetes Vulnerabilities - Main Takeaways
Stranger Danger: Your Java Attack Surface Just Got Bigger
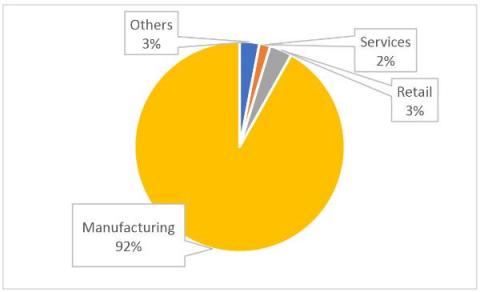
73 Percent Of Retail Applications Contain Security Flaws, But Only A Quarter Are Fixed
How to use GitHub Actions environment variables
To improve the efficiency of releasing working code into a production environment, implementing a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline is a great practice. These pipelines automate the process of checking that a code change is ready for release and provides tools to automate the release to a production environment. One popular way to do this is to use your existing version control system.
Top 10 Exploited Vulnerabilities in 2022
With each passing year, hacker attacks become more advanced and sophisticated, so keeping up with security vulnerabilities is now more crucial than ever. This article highlights some of the most dangerous vulnerabilities exploited by malicious actors in 2022.
Beyond NVD data: Using Black Duck Security Advisories for version accuracy
80% of SMBs Are Vulnerable - Here's How to Stay Safe
It would be nice to imagine that when cyber criminals look for their next target, they ignore the small- and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) that simply can’t afford an attack. Unfortunately, that’s not the case. In fact, 43% of cyber attacks are directed at SMBs. Today, a massive 80% of North American SMBs are at risk of a cyber attack.
How to write tests in Python using doctest
As developers, we often write test cases and comments to explain our code. Commenting improves the codebase’s readability and quality. Detailed comments can remind us why we implemented a specific functionality. They can also help other programmers understand, maintain, use, and expand codebases.
Writing unit tests in Java
Testing is a crucial best practice when developing software. Unit testing is one of the numerous strategies we can use to ensure our code is functional and optimal. As developers, we can code unit tests to check individual components (units) of the application code, such as a specific method. The idea is to write one or more unit tests for each code section and run them every time a change is made to catch defects as soon as they are introduced into the codebase.
Anatomy of a Stored Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability in Apache Spark
One of the services that Veracode offers is a consultation with an Application Security Consultant – a seasoned software developer and application security expert. In the context of a consultation, my team works with the software engineers of Veracode’s customers to understand and, ideally, remediate security flaws found by the Veracode tool suite.
Dependency injection in JavaScript
Inversion of control (IoC) techniques give developers a way to break out of traditional programming flow, and it offers them more flexibility and greater control over their code. Dependency injection, one form of IoC, is a pattern that aims to separate the concerns of constructing objects and using them. In this article, you’ll learn what dependency injection is, when you should use it, and what popular JavaScript frameworks it’s implemented in.
Setting up SSL/TLS for Kubernetes Ingress
Today, web and mobile applications and API-based microservice endpoints are becoming the default. These applications are reachable through the HTTP web protocol. The encryption provided by a Secured Socket Layer or Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) is a must to secure the communication between client and server and across API back-ends. SSL/TLS are certificate-based encryption mechanisms. SSL has been the standard for over 20 years.
This Feels Scripted: Zeek Scripting and Splunk
I originally planned to write this story as a follow-up to another blog that SURGe released for CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786 (aka SpookySSL). That blog mentions that we weren’t able to test with any malicious payloads yet, and as things go… After releasing that blog, we came across proof-of-concept exploits that weren’t detected by our searches.
Windows 10 most critical vulnerabilities in 2022
How Atlassian used Snyk to solve Log4Shell
Snyk recently launched a multi-day live hack series with AWS, where experts demonstrated exploits in real-time and explained how to defend against those vulnerabilities. This series helped viewers discover new ways to improve security across the application stack for AWS workloads. As part of the series, Micah Silverman (Director of Developer Relations, Snyk) and Chris Walz (Senior Security Engineer, Atlassian) discussed Log4Shell.
Best practices for Kubernetes Secrets management
Kubernetes uses secret objects, called Secrets, to store OAuth tokens, secure shell (SSH) keys, passwords, and other secret data. Kubernetes Secrets allow us to keep confidential data separate from our application code by creating it separately from pods. This segregation, along with well-formed role-based access control (RBAC) configuration, reduces the chances of the Secret being exposed — and potentially exploited — when interacting with pods, thereby increasing security.
PyPi Malware Stealing Discord and Roblox Payment Info
Stranger Danger: Your JavaScript Attack Surface Just Got Bigger
The "Software Vulnerability Snapshot" reports that 95% of tests uncovered vulnerabilities in target apps
Learn about the key takeaways from the “Software Vulnerability Snapshot” report, which examines security issues uncovered in web and mobile apps.
Turns out 78% of reported CVEs on top DockerHub images are not really exploitable
Similarly to our previous research on “Secrets Detection,” during the development and testing of JFrog Xray’s new “Contextual Analysis” feature, we wanted to test our detection in a large-scale real-world use case, both for eliminating bugs and testing the real-world viability of our current solution.
5 best practices for building modern access control for cloud applications
Recently, I met with Or Weis — a Snyk Ambassador — to discuss access control in the cloud. Or is an entrepreneur, based in Tel Aviv, where he founded Permit.io, a solution that empowers developers to bake in permissions and access control into any product in minutes and takes away the pain of constantly rebuilding them.
4 Reasons Scan Results May Differ Over Time: Advice from an Application Security Consultant
You didn’t change anything in your code, yet the scan is different this time. Here’s advice from an Application Security Consultant on why that may be. Have you ever wondered why you scan code one day and get one result, and then scan the same code a month later and get different results – even though you never changed anything?
Stories from the SOC: Fortinet authentication bypass observed in the wild
Fortinet’s newest vulnerability, CVE-2022-40684, allowing for authentication bypass to manipulate admin SSH keys, unauthorized downloading of configuration files, and creating of super admin accounts, has put a big target on the backs of unpatched and exposed Fortinet devices.
SREs bring O.R.D.E.R(R) to C.H.A.O.S - Snyk Ambassadors Show
Cloud security fundamentals part 5: measure what matters
Many security engineers have woken up to dozens of Slack messages and emails telling them the day they dreaded is here: a vulnerability has been deployed, and now it must be fixed. Meetings and plans are abandoned while security engineers rush to fix the problem. It’s often a process failure that has led to the now-urgent issue. And these emergency issues can appear across a spectrum that includes all types of remediation efforts.
Three Critical Vulnerabilities Impacting VMware Workspace ONE Assist Server CVE-2022-31685, CVE-2022-31686 and CVE-2022-31687
Using Sysdig Secure to Detect and Prioritize Mitigation of CVE 2022-3602 & CVE 2022-3786: OpenSSL 3.0.7
The awaited OpenSSL 3.0.7 patch was released on Nov. 1. The OpenSSL Project team announced two HIGH severity vulnerabilities (CVE-2022-3602, CVE-2022-3786), which affect all OpenSSL v3 versions up to 3.0.6. These vulnerabilities are remediated in version 3.0.7, which was released Nov. 1. The vulnerabilities fixed include two stack-based buffer overflows in the name constraint checking portion of X.509 certificate verification.
Implementing TLS in Java
TLS, or transport layer security, is a protocol used across the globe to encrypt and secure communication over the internet. In this article, we’ll discuss what TLS is, what benefits it provides, and why you need it. Then we’ll walk through implementing TLS in Java.
How to Modernize Access Control for Cloud Applications with Or Weis
Introduction to Snyk's revamped reporting
CVE-2022-27510: Citrix Gateway and Citrix ADC Critical Authentication Bypass Vulnerability, along with CVE-2022-27513 & CVE-2022-27516
Six Actively Exploited Vulnerabilities Patched in Microsoft's November Security Update
Denial Of Service vulnerabilities
SnykLaunch Fall 2022 Helps Companies Successfully Drive DevSecOps
JFrog's security scanners discovered thousands of publicly exposed API tokens - and they're active! The Full Report
Note: This report was previously published in InfoWorld When developing the recently announced JFrog Advanced Security, our Research team decided to try out its new “Secrets Detection” feature. Our goal was to test our vulnerability detection on as much real world data as possible, to make sure we eliminate false positives and catch any bugs in our code.
Supply chain integrity, transparency and trust is now firmly on the agenda
Supply chain risk continues to make headlines, from Solarwinds and Kaseya to last week’s announcement of a patch for the OpenSSL vulnerability, and the latest cybersecurity review from the U.K.’s National Cyber Security Centre highlights the serious threats posed by supply chain attacks.
Secure Coding in C and C++ Using Fuzz Testing
Today, I would like to show you to a simplified fuzz testing approach that enables secure coding of C and C++ applications. If you read this article to the end, you will learn about an automated security testing approach for C/C++ that can protect your applications against all sorts of memory corruptions and other common C/C++ vulnerabilities.
SnykLaunch recap: Snyk Cloud, SBOM & reporting capabilities, and customer solutions resources
At SnykLaunch on November 8th, our product leaders unveiled the latest additions to Snyk’s suite of developer-first products. We also gave viewers a sneak peek of these new features in action with live demos. We’re especially excited to announce Snyk Cloud, our cloud security tool that takes a contextual approach to finding and fixing cloud vulnerabilities.
Holm Security adds Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) to its portfolio at the Gartner IT Symposium/Xpo Conference 2022
Key points from Google and Accenture's ransomware white paper
Ransomware has been around for a long time — since 1989 — but has scaled up significantly since 2016. Author’s from Accenture and Google Cloud, in addition to our very own Vandana Verma Sehgal (from the Snyk Security Relations Team), recently released a white paper, Ransomware State of Mind: How to Better Protect Your Business, which details the current state of ransomware and solutions to address this growing problem.
NPM security: preventing supply chain attacks
NPM security has been a trending topic in the media in recent years, mostly in reference to npm packages available on the ecosystem rather than the npm registry itself. The increasing security risk, that applies to developers and software we build, makes it even more important to understand how to prevent supply chain attacks and other security vulnerabilities related to software development life cycle.
How They Started in Cybersecurity - Snyk Ambassadors Show
Why is CREST OVS Important?
The CREST (Council Registered Ethical Security Testers) OVS (OWASP Verification Standard) has been created to help standardise the way that advanced penetration tests are executed by creating a framework for all security consultancies to follow.
Breaking down the 'critical' OpenSSL vulnerability
On November 1st 2022, the OpenSSL team released an advisory detailing two high severity vulnerabilities — CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786. This was pre-announced as a critical bug, but later downgraded to high for the actual release. This could still be problematic though, OpenSSL is one of the predominant encryption libraries and is underpinning a significant portion of the internet’s TLS protected communications.
Vulnerability Management: The Beginner's Guide
As available software on the market increases, so do vulnerabilities. When a company's system is weak due to vulnerabilities in the software it uses, attackers take advantage of the situation to: This, in turn, causes the company to lose customers, reputation and money. To reduce threats, network personnel and system administrators are always on the front line, constantly patching the organization's software and operating systems. But to what end?
Cloud security fundamentals part 4: Align and automate with policy as code
Security policies are still awaiting digital transformation. A key phrase in today’s cloud-driven world, “digital transformation” generally refers to the ongoing work of digitizing formerly paper-based processes. “Paper,” however, is not literal — many processes don’t use paper, but still flow as if they were. Uploading a document to Google Drive, in other words, doesn’t amount to digital transformation.
Understanding NPM Dependency Confusions - What You Need to Know
CyRC Vulnerability Advisory: CVE-2022-43945 buffer overflow vulnerabilities in NFSD
Secure Python URL validation
Everything on the internet has a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that uniquely identifies it — allowing Internet users to gain access to files and other media. For instance, this article has a unique URL that helps search engine optimization (SEO) crawlers index it for users to find. The first definition of the URL syntax is in the 1994 Request for Comments (RFC) 1738. Since then, the structure of URLs has gone through many revisions to improve their security.
The New OpenSSL Vulnerabilities: How to Protect Your Business
The OpenSSL project has announced two security vulnerabilities tracked as CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786. The good news is that these vulnerabilities are unlikely to facilitate remote code execution as originally anticipated, and only OpenSSL version 3.0.0 and later are impacted. The bad news, however, is that even though the remote control is unlikely, it’s still possible.
Pentesting as a Service for Web Applications
Update: OpenSSL high severity vulnerabilities
OpenSSL has released two high severity vulnerabilities — CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786 — related to buffer overrun. OpenSSL initially rated CVE-2022-3602 as critical, but upon further investigation, it was reduced to high severity.
Vulnerability vs. Threat vs. Risk vs... "Other"
In cybersecurity, three key terms are vulnerability, threat and risk. Often they’re tossed around interchangeably, but they have a specific relationship to one another..
OpenSSL CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786 (Spooky SSL): What They Are and How to Mitigate Risk
On November 1, OpenSSL v3.0.7 was released, patching two new high-severity vulnerabilities: CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786. The new vulnerabilities have been dubbed by the community as “Spooky SSL,” although the name is not recognized by the OpenSSL team. CVE-2022-3602 was originally discovered by a researcher known as Polar Bear, while CVE-2022-3786 was found during the analysis of the first vulnerability by Viktor Dukhovni.
CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786 - High-severity OpenSSL Vulnerabilities Finally Published
On October 25th, The OpenSSL team announced that OpenSSL 3.0.7 will contain a fix for a critical severity vulnerability that affects OpenSSL 3.x. The full details about the vulnerability were held in an embargo until November 1st. Due to the rarity of an OpenSSL critical-severity issue and the overwhelming popularity of OpenSSL, social media was flooded with messages about this issue, expecting a “Log4Shell”-level event.
Stranger Danger: Your JavaScript Attack Surface Just Got Bigger
CVE-2022-3602 and CVE-2022-3786 - OpenSSL 3.0.X Critical Vulnerabilities
Ruby on Rails Docker for local development environment
Hi there Ruby developers! If you’ve been looking for an effective way to establish a Ruby on Rails Docker setup for your local development environment, then this post is for you. It’s a continuation of our previous article on how to install Ruby in a macOS for local development. Ruby developers frequently need to account for a database when building a Ruby on Rails project, as well as other development environment prerequisites.
CVE-2022-36537 - Critical RCE Vulnerability & Supply Chain Risks in ConnectWise Recover and R1Soft Server Backup Manager
Cybersecurity Awareness Month: Adding Threat to Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management can be more than just running scans and sorting by Common Vulnerability Scoring System scores! Take your program to the next level by adding a threat-based approach to vulnerability management by combining the hacker mindset with cyber threat intelligence. With so many vulnerabilities published daily, having a team knowledgeable with the latest threats can help IT teams quickly identify assets that require expedited remediation.
What You Need to Know About OpenSSL-3.0.7
OpenSSL released version 3.0.7 with security fixes for High Severity vulnerabilities CVE-2022-3786 & CVE-2022-3602 discussed here. Here's how to know if you're affected and what to do if you are.
5 Steps to Stop the Latest OpenSSL Vulnerabilities: CVE-2022-3602, CVE-2022-3786
The OpenSSL Project team announced two HIGH severity vulnerabilities (CVE-2022-3602, CVE-2022-3786) on October 25, which affect all OpenSSL v3 versions up to 3.0.6. These vulnerabilities are remediated in version 3.0.7 which was released November 1. OpenSSL 1.X versions are unaffected by the vulnerabilities.