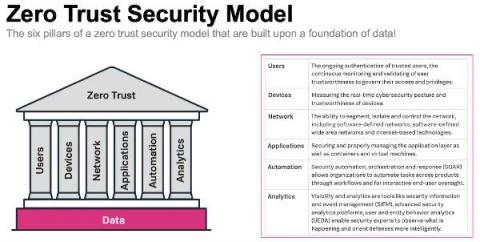
Why the Evolution of Zero Trust Must Begin with Data Protection
The need for “Zero Trust” today is no longer the same as what we talked about years ago when the term was first coined. Back then, businesses only had a handful of remote workers signing in to the corporate network. The common wisdom of the day dictated that you couldn’t implicitly trust the authentication of those remote users any longer because they weren’t on the company LAN and the common solution was installing two-factor authentication.