Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
Latest News
Developer-first Security sucks! Why is it essential to automate product security?
Security teams focus on planning secure IT environments, but developers are asked to focus on productivity while they are also tasked with implementing these security plans. The main issue is that developers are often left out of security planning processes, creating a strained relationship between these two teams.
Checksum: How does it ensure security for your vital data?
A checksum is small code of computed information that deals with data integrity and security. It is vital for huge data files (in gigabytes) being downloaded from any online site. It checks whether the downloaded file is missing any bytes and is downloaded correctly. The checksum value changes even if there is a small change in the downloaded file or data.
Difference Between Black-Box Testing & White-Box Testing
A developer goes through different development and deployment rules for creating applications. Testing is an essential step in the development cycle. When it comes to software testing, many techniques need to be used from time to time. Yet the confusion around white, grey, and black testing techniques are most common among all software testing techniques. They often appear similar, yet the differences between them are very jarring.
The New Kubernetes Gateway API and Its Use Cases
A CISO's Guide to Container Security: Understanding Vulnerabilities & Best Practices
Companies are introducing new apps and services to enable remote work, improve supply chains and handle disruptions caused by the pandemic. Our digital-first world thrives on speed and efficiency, and containers play a huge part in getting applications up and running quickly. Though containers offer many advantages over traditional virtualization, they also introduce significant security risks.
The future of email threat detection
As businesses continue to adopt cloud integration and remote work increases, security teams are facing more visibility challenges as well as an influx of security event data. There is more need to understand the threats than ever before, as the threat surface area increases, and tactics increase. Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated and occurring more frequently, forcing organizations to rely on quality threat detection to protect their data, employees, and reputation.
Securing MySQL Databases with SSL/TLS.
Many databases were born over 25 years ago, back in the unadulterated times of LAN parties and IRC. SSL was just for banks and sending unencrypted database traffic accounts was just how you did things. When databases use unencrypted connections, it means someone with access to the network could watch all and inspect all database traffic.
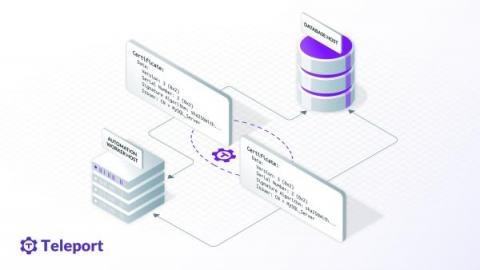
Production MySQL SSL with Teleport Machine ID
In the first part of this blog post, we setup SSL/TLS for a MySQL database, using the built in self-signed certificates. The main problem using out of the box self-signed certificates is that clients can't verify that they're talking to the right database host, and it's not possible to verify the certificate chain. In this post we'll cover upgrading the client connection to VERIFY_IDENTITY and how to use Machine ID to continuously renew certificates.
Wet signatures cost more than you might think
Speaking to people on our neighbouring booths at the UK nuclear decommissioning event, it was clear to see the entire industry is drowning in paperwork.