Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
Latest News
How COVID-19 Affected and Caused Cyberattacks on Hospital Systems
Meeting the Third-Party Risk Requirements of the CCPA in 2022
Often regarded as the Californian version of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) aim’s to increase consumer rights by giving California residents greater control over the use of their personal data. The CCPA heavily regulates the use of any data that could potentially link to the identity of a consumer or household, either directly or indirectly.
What's the Difference Between 2FA and MFA?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a type of multi-factor authentication (MFA). Both authentication solutions provide additional account security by requiring additional factors of authentication. To understand how exactly 2FA and MFA differ, it’s firstly important to understand the concepts of authentication and factors of authentication.
What is Shadow IT? When Staff Revolt Against the IT Department
Shadow IT includes any unsanctioned apps or hardware used by employees that fall outside of those managed by the IT department (sanctioned apps). Shadow IT is often used as a workaround to functionality or usability gaps created by an organization’s known IT resources. Large organizations have multiple departments with widely differing information technology (IT) needs.
Meeting the 3rd-Party Risk Requirements of The NY SHIELD Act
The Stop Hacks and Improve Electronic Data Security (SHIELD) Act is designed to protect the personal data of all New York residents. This act broadens the data privacy and protection standards stipulated in the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and the New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS). What makes this particular data protection law unique is its inclusion of biometric information, usernames, and passwords in the category of personal information.
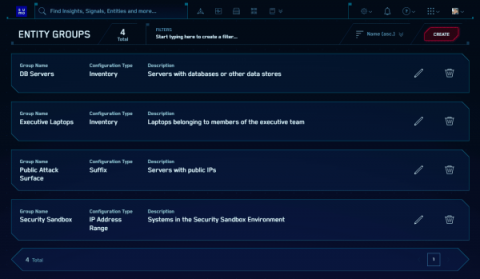
Use new Cloud SIEM Entity Groups to make threat response more efficient
Nightfall vs. Aware: Looking for an alternative to Aware?
Most companies are determined to make remote work feasible for the future. To do so, they need the right tools to maintain data security while their employees work here, there, and everywhere. There are many tools on the market that enable cloud security, and understanding which options are right for your business can be confusing. Different vendors offer different features, compliance with different regulations, levels of complexity, and types of coverage.