Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
October 2022
Stolen Passwords and Ransomware Attacks: How Small Businesses Can Protect Themselves
Stolen passwords and compromised credentials are among the leading causes of ransomware attacks. In 2021, the IC3 received 3,729 complaints identified as ransomware, with more than $49.2 million in adjusted losses. Startups and small business enterprises (SMEs) must take preventative measures to lower their risk of a ransomware attack. Keep reading to learn more about ransomware and what steps your company can take to protect itself.
The 443 Podcast Episode 215 - CISA's Cybersecurity Performance Goals
The Simply Cyber Report: October 31, 2022
The recovery: How to overcome a malware attack
A report published by Cybersecurity Ventures predicts that by 2031, ransomware will attack a business, individual, or device every two seconds. The consequences of such an attack extend beyond the leak of sensitive information and financial losses; customers and clients don’t want to do business with organizations that neglect security of customer data. You can’t simply hope an attack will never happen.
Increase Internet Security While Browsing Online With Proper Antivirus - Top 3 Picks
CrowdStrike Falcon Platform Achieves 100% Ransomware Prevention with Zero False Positives, Wins AAA Enterprise Advanced Security Award from SE Labs
The CrowdStrike Falcon platform delivered 100% ransomware detection and protection with zero false positives in winning the AAA Enterprise Advanced Security (Ransomware) Award in the first-ever SE Labs EDR ransomware evaluation.
How Egnyte Uses AV-Service to Detect Malware
In hybrid or remote desktop environments, content is the most exposed type of data. Egnyte’s all-in-one platform makes it simple and easy for IT to manage and control a full spectrum of content risks, including accidental data deletion, data exfiltration, privacy compliance, and much more. All while giving business users the tools they need to work faster and smarter—from any cloud, any device, anywhere.
Your Cybersecurity MVP: the Rubrik Ransomware Response Team
Have you ever asked yourself, “What happens if I am attacked by ransomware?” Well, the over 4,500 Rubrik customers around the world have the ultimate peace of mind knowing their data is secure with our Zero Trust Data Security platform. In addition to Rubrik’s industry-leading and comprehensive data security solution, we also have a specialized Ransomware Response Team to provide world-class support and care when our customers are attacked.
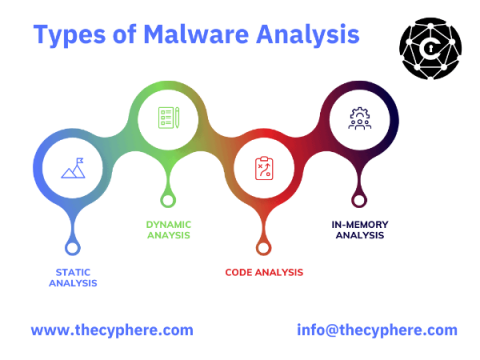
Malware Analysis Guide: Types & Tools
Malware analysis is a process of identifying and examining malware samples to understand the threat they pose. This information can develop defences against the malware or help remove it from infected systems. Malware analysis is a critical skill for incident responders and IT professionals. There are a variety of malware analysis tools and techniques that can be used, depending on the type of malware sample.
Playing Hide-and-Seek with Ransomware, Part 2
In Part 1, we explained what Intel SGX enclaves are and how they benefit ransomware authors. In Part 2, we explore a hypothetical step-by-step implementation and outline the limitations of this method. Watch this live attack demo to see how the CrowdStrike Falcon® platform and the CrowdStrike Falcon Complete™ managed detection and response team protect against ransomware.
DevOps backups vs. ransomware - best security and compliance practices
Archive Sidestepping: Self-Unlocking Password-Protected RAR
Trustwave SpiderLabs’ spam traps have identified an increase in threats packaged in password-protected archives with about 96% of these being spammed by the Emotet Botnet. In the first half of 2022, we identified password-protected ZIP files as the third most popular archive format used by cybercriminals to conceal malware.
Rubrik and GraphQL - Episode 6 - Using the Rubrik API Code Capture Extension
Conquer the Three Battlegrounds of Modern Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
One of the most empowering documents in an organization’s arsenal is its business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) plan. Sure, it lays out in detail everything bad that could happen to your business, but it also provides point-by-point strategies to respond to each of those threats. Or does it? A good BCDR plan is a living document that evolves alongside the threats its organization faces. The trouble is that the world is changing fast, and BCDR teams are breathlessly trying to keep up.
Despite Lowest Software Flaw Frequency, Manufacturing's Fix Times Lag and Create Ransomware Risk
In 2021, manufacturing became cybercriminals’ most targeted industry as a surge in global ransomware attacks disrupted manufacturing operations and exacerbated supply chain woes. This put even more pressure on manufacturing organizations that were already feeling the heat. Recognizing that ransomware attacks can stem back to software vulnerabilities, many manufacturers are exploring ways to strengthen their software security programs.
Infrastructure Security is Not Enough to Defend Against Ransomware
Register Now Let’s face it, you’re still vulnerable to ransomware. Even if it feels like you’ve done everything—you’ve built a robust defense, you have multiple cybersecurity measures in place, and you’ve implemented a company-wide security training. But, is it enough? Every business is vulnerable to ransomware. From the largest bank to the smallest school.
Why Auto Dealers Are Prime Targets for Ransomware Attacks
Cybersecurity Insights: Secure Your Clients Against Ransomware
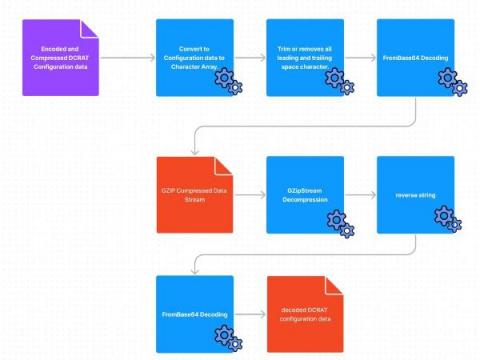
Dark Crystal RAT Agent Deep Dive
The Splunk Threat Research Team (STRT) analyzed and developed Splunk analytics for this RAT to help defenders identify signs of compromise within their networks. Remote Access Trojans (RATs) are one of the most common tools used by threat actors as a malicious payload to attack targeted hosts and steal information. One example is the Dark Crystal RAT (DCRat) that is capable of remote access, post exploitation and data exfiltration.
Stories from the SOC: Feeling so foolish - SocGholish drive by compromise
SocGholish, also known as FakeUpdate, is a JavaScript framework leveraged in social engineering drive by compromises that has been a thorn in cybersecurity professionals’ and organizations’ sides for at least 5 years now. Upon visiting a compromised website, users are redirected to a page for a browser update and a zip archive file containing a malicious JavaScript file is downloaded and unfortunately often opened and executed by the fooled end user.
Rubrik + Microsoft Sentinel: Get a head start in the race against ransomware
According to Statistica, the average response time to a ransomware attack is 20 days. 20 days where your customers can’t order your product, 20 days where your end-users are unable to access important information - 20 days of incurred downtime for your organization resulting in massive profit losses and reputation damage. I think it goes without saying, time is of the essence during a ransomware attack.
The Anatomy of Wiper Malware, Part 4: Less Common "Helper" Techniques
In Part 3, CrowdStrike’s Endpoint Protection Content Research Team covered the finer points of Input/Output Control (IOCTL) usage by various wipers. The fourth and final part of the wiper series covers some of the rarely used “helper” techniques implemented by wipers, which achieve secondary goals or facilitate a smaller portion of the wiping process.
Why Data Security is So Important
Register Now Nearly every day, news articles showcase big-name companies that became victims of cyberattacks and the hundreds of millions of dollars of loss it will have on their business. These headlines should not be surprising when you look at the data. The number of ransomware detected in Q1 2022 alone was double that of the whole year of 2021.
Save the Data
Playing Hide-and-Seek with Ransomware, Part 1
At CrowdStrike, our mission is to stop breaches. To achieve this, we’re always on the lookout to defend customers against active attacks and preemptively protect them against emerging threats. In July 2021, researchers from Royal Holloway, University of London, published a white paper, “RansomClave: Ransomware Key Management using SGX,” that presents a novel ransomware based on an Intel feature called Software Guard Extension (SGX).
Introducing GraceWrapper, TA505's sophisticated post-exploitation enabler
Since its inception almost a decade ago and the MirrorBlast campaign, the threat actor group known as TA505 has continued to plague the financial, retail and restaurant sectors.
WDigest Clear-Text Passwords: Stealing More than a Hash
Digest Authentication is a challenge/response protocol that was primarily used in Windows Server 2003 for LDAP and web-based authentication. It utilizes Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Simple Authentication Security Layer (SASL) exchanges to authenticate. At a high level, a client requests access to something, the authenticating server challenges the client, and the client responds to the challenge by encrypting its response with a key derived from the password.
Combat Ransomware with Zero Trust Data Security
Can’t see the forest through the trees. Can’t tell the ransomware from the apps. Can’t contain the malware if you can only see parts of the network. Ransomware hackers have several different tools in their toolbelt to gain access to a computer and then a network. Common exploits include email phishing campaigns, remote desktop protocol (RDP) vulnerabilities, and software vulnerabilities.
[Webinar] DevOps backups vs. ransomware - best security and compliance practices.
Ransomware - undeniably top of mind
Ransomware’s first documented attack was relatively rudimentary. It was delivered via floppy disk containing a malware program in 1989 that told its victims to pay $189 in ransom to a PO Box in Panama. Today ransomware criminals are significantly more sophisticated, thanks to advances in cyber methods and cryptocurrencies. Not all Ransomware is created equally. Like all malware, malicious codes vary in sophistication and modularity. As such, not all ransomware codes are made the same.
Top Web Application Security Threats Review
7 Biggest Cybersecurity Threats of the 21st Century
The 21st century has seen a dramatic increase in the number and sophistication of cybersecurity threats. Here are the 7 biggest threats that businesses and individuals need to be aware of.
Q3 Ransomware Landscape Report
Fortify & Secure Your Kubernetes Environment with Rubrik Security Cloud
Enterprises have benefited from encapsulating applications into lightweight, independent units called microservices. By adopting an architectural pattern of loosely coupled and independently deployed services, microservices can rapidly deliver complex applications at scale without the typical technical debt of legacy applications.
Unstoppable: Conversations About Data Security Ep. 1 | Why Defense Wins Games
Ransomware Losses Prompting Cyber Insurers to Raise Rates and Slash Coverage
The year 2021 had the dubious distinction of being the most prolific for ransomware on record, and the onslaught didn’t stop in 2022. It’s now estimated that every 14 seconds, a business falls victim to a ransomware attack. Ransomware attacks aren’t just happening more often.
Deliver a Strike by Reversing a Badger: Brute Ratel Detection and Analysis
A new adversary simulation tool is steadily growing in the ranks of popularity among red teamers and most recently adversaries. Brute Ratel states on its website that it "is the most advanced Red Team & Adversary Simulation Software in the current C2 Market." Many of these products are marketed to assist blue teams in validating detection, prevention, and gaps of coverage.
RedLine Stealer Campaign Abusing Discord via PDF Links
RedLine is an infostealer malware discovered in 2020. Often sold in underground forums, it is capable of stealing data such as credit card numbers, passwords, VPN and FTP credentials, gaming accounts, and even data from crypto wallets. In May 2022, Netskope Threat Labs analyzed a RedLine stealer campaign that was using YouTube videos to spread, luring victims into downloading a fake bot to automatically buy Binance NFT Mystery Boxes.
Why Security Should be Design Principle Number One
National Cybersecurity Awareness Month (NCSAM), held every October, highlights a key theme each year. For 2022, the theme is: “See Yourself in Cyber.” Cybersecurity is more than a set of principles or tools—people are a major component, helping keep businesses safe by complying with multi-factor authentication, using strong passwords, keeping devices updated with the latest software, not installing unapproved software on devices, and reporting phishing.