Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
Zero Trust
Unlocking The Power of Zero with Netskope and Okta
We need to shift how we as security practitioners break the barriers for collective threat awareness across identity touchpoints within cybersecurity. It’s become imperative that we gain the ability to continuously assess user risk with automatic response actions—a shift towards a unified, contextually-driven identity defense.
Provide Remote Access with a Zero Trust Solution
The Role of UEBA in Zero Trust Security
As cyber threats have grown in sophistication and frequency, a paradigm shift in security strategy has become imperative. This shift has given rise to the Zero Trust Security Framework, an approach that challenges the very foundation of trust in network security. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) steps into the spotlight as a dynamic force that complements and enhances the Zero Trust Security framework. Let’s discover how UEBA can help organizations achieve zero trust security!
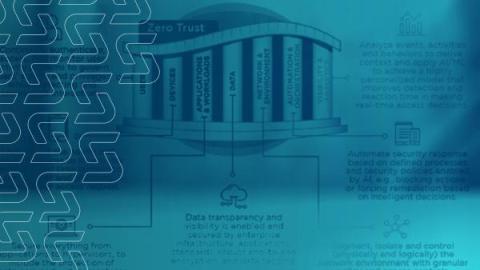
PAM360 Zero Trust Overview
What is Zero Trust
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity philosophy that rejects the idea of offering implicit trust to traffic based on network location. In other words, Zero Trust views all traffic as potentially malicious, regardless of whether it originates from a traditionally trusted network source, and therefore requires all traffic to be scrutinized to determine whether access should be granted to a specific resource.
Cloudflare One - Zero Trust Platform Overview
Why EDR and NDR Tools Are Not Zero Trust Security Solutions & What to Use Instead
Lock the doors inside your home, hand out keys sparingly, then turn on an alarm in every room. Your house will get a lot more secure. However, it will also become unlivable. Tight security policies, access conditions, and subnetting configurations can take away risk but even mature Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) environments must balance cybersecurity with usability.
Why Traditional Security Solutions Don't Fit Zero-Trust Architecture
“Just make us Zero Trust.” Hands up if you’ve ever heard some version of this statement. Gather ten cybersecurity pros in a room, and you’ll have ten frustrated people trying to implement Zero Trust Security Architecture (ZTA). Although boards and non-security executives often understand the ZTA security model at a high level and love the idea of an inherently secure network, security teams keep running into walls during implementation.
The Crucial Role of Identity in Zero Trust Security
In an increasingly digital world where cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, organizations are embracing new strategies to protect their sensitive data and assets. One such approach that has gained prominence in recent years is Zero Trust. Zero Trust challenges the traditional perimeter-based security mindset and instead places a strong emphasis on identity as a cornerstone of a robust defense strategy.