Forward Networks Delivers First Generative AI Powered Feature
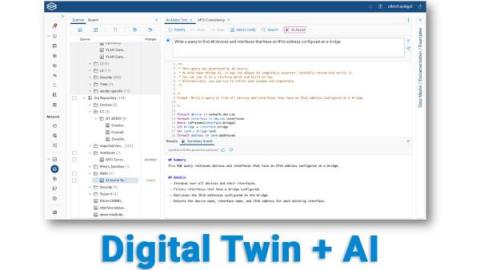
Natural language prompts put the power of NQE into the hands of every networking engineer As featured in Network World, Forward Networks has raised the bar for network digital twin technology with AI Assist. This groundbreaking addition empowers NetOps, SecOps, and CloudOps professionals to harness the comprehensive insights of NQE through natural language prompts to quickly resolve complex network issues. See the feature in action.