Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
%term
How to use Kibana effectively. Today: Detect possible frauds in your data
Foundational Controls Make the Hard Things Easier to Do
Let’s begin with a short story. Imagine that we have two large organizations in the public sector. These entities are very similar. Both are on the receiving end of cyber threats. Both adhere to multiple compliance standards. And both need to ensure that their IT systems are functioning and working as planned. But they’re not entirely the same. Take Organization A, for example.
Protect Your AWS Infrastructure with GuardDuty and Coralogix
Cloud environments like AWS can be a challenge for security monitoring services to operate in since assets tend to dynamically appear and disappear. Making matters more challenging, some asset identifiers that are stable in traditional IT environments like IP addresses are less reliable due to their transient behavior in a cloud service like AWS. Amazon GuardDuty protects your AWS environment with intelligent threat detection and continuous monitoring.
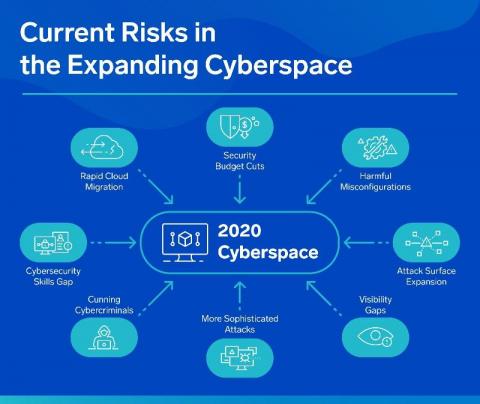
Why cloud-native SIEM is vital to closing the security skills gap
How to Reduce the Risk of Misoperations in Your Bulk Electric Systems
Reliability is essential to the functionality of an electric power grid. This principle guarantees that a constant qualitative and quantitative supply of electric power is flowing from a provider to businesses, homes and more. It’s what enables electric power to drive life forward in modern society. As a result, there’s reason to be concerned about events that threaten the reliability of the power grid. Those events include misoperations.
Webinar: AIOps Outcome - Asset dependency insights | CloudFabrix
Why Data Security is Gaining Traction
Bloor Research: what makes a good MDR service?
The diverse and fast-changing nature of the Managed Detection and Response (MDR) market makes the process even more difficult. A new report, MDR Market Guide: reducing the costs and risks of cybersecurity investments, from independent technology research and analyst house, Bloor, outlines the key features to consider when selecting an MDR provider.
What quantum cryptography means for cybersecurity
Just as cybersecurity professionals are getting used to the possible implications of quantum computers, a new front opens in the quantum arms race: using quantum computers for encryption. Though quantum computers remain a largely theoretical threat, some researchers are already working on ways to protect systems against the exponential increase in computing power they represent.