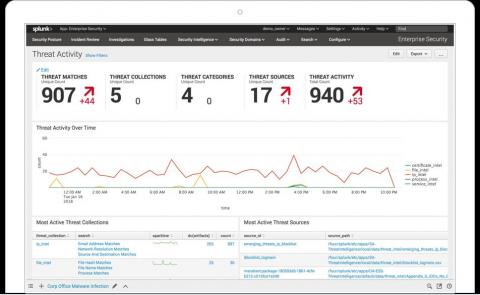
Security operations: Cloud monitoring and detection with Elastic Security
As many organizations have migrated their infrastructure, applications, and data to cloud offerings, adversaries have extended their operational capabilities in cloud environments to achieve their mission — whether that means stealing intellectual property, disrupting business operations, or holding an organization’s data for ransom.