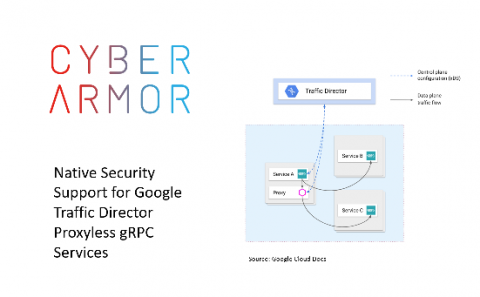
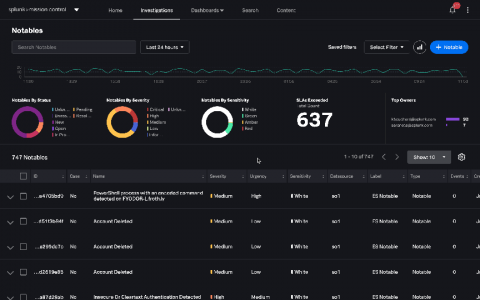
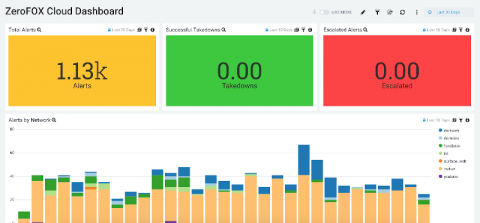
Effective Threat Intelligence Through Vulnerability Analysis
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses leveraged by adversaries to compromise the confidentiality, availability or integrity of a resource. The vulnerability ecosystem has matured considerably in the last few years. A significant amount of effort has been invested to capture, curate, taxonomize and communicate the vulnerabilities in terms of severity, impact and complexity of the associated exploit or attack.