Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
Threat Hunting
Falcon OverWatch Threat Hunting Contributes to Seamless Protection Against Novel BlackCat Attack
In an effort to stay ahead of improvements in automated detections and preventions, adversary groups continually look to new tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs), and new tooling to progress their mission objectives. One group — known as BlackCat/ALPHV — has taken the sophisticated approach of developing their tooling from the ground up, using newer, more secure languages like Rust and highly customized configuration options per victim.
Falcon Complete: A Pioneer in MDR
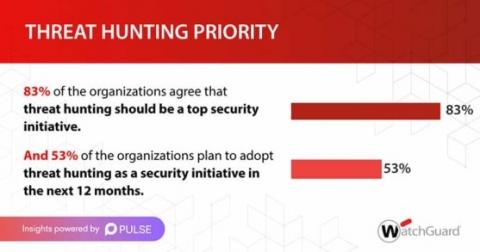
How are IT leaders approaching threat hunting?
Implementing robust defense strategies helps to mitigate the risk of cyberthreats in the early stages of an attack. Threat hunting, as part of this strategy, enables organizations to find those unknown threats that manage to bypass technology-based controls by detecting abnormal behaviors. With a number of challenges associated with executing a defense approach, how are IT leaders approaching this problem? Pulse and WatchGuard surveyed 100 IT leaders to find out.
Falcon OverWatch Threat Hunting Uncovers Ongoing NIGHT SPIDER Zloader Campaign
Over recent months, the CrowdStrike Falcon OverWatch™ team has tracked an ongoing, widespread intrusion campaign leveraging bundled.msi installers to trick victims into downloading malicious payloads alongside legitimate software. These payloads and scripts were used to perform reconnaissance and ultimately download and execute NIGHT SPIDER’s Zloader trojan, as detailed in CrowdStrike Falcon X™ Premium reporting.
Hunting pwnkit Local Privilege Escalation in Linux (CVE-2021-4034)
In November 2021, a vulnerability was discovered in a ubiquitous Linux module named Polkit. Developed by Red Hat, Polkit facilitates the communication between privileged and unprivileged processes on Linux endpoints. Due to a flaw in a component of Polkit — pkexec — a local privilege escalation vulnerability exists that, when exploited, will allow a standard user to elevate to root.
Why should you include threat hunting services in your portfolio?
As mentioned in our previous blog post about threat hunting, there is significant interest in it. In fact, according to Pulse, 32% of IT leaders say that their organizations plan to reinforce their endpoint security posture by adding a threat hunting program to their overall security strategy. And it is not surprising since it is a potent tool to defend your customer. Here we have some of the key benefits that hunting brings to your value-added services.
Trustwave Threat Hunting Guide: Identifying PwnKit (CVE-2021-4034) Exploitation
The Trustwave Threat Hunting team has authored a practical guide to help the cybersecurity community address the Linux “polkit” Local Privilege Escalation vulnerability (CVE-2021-4034) by identifying common behavior in exploitation.
Threat hunting: a top priority for businesses of all sizes
Today's threat actors are well-organized, highly skilled, motivated, and focused on their targets. These adversaries could be lurking on your network or threatening to break into it, using increasingly sophisticated methods to reach their goal. Simply put, there's often no need for adversaries to deploy malware at the early stages of the attack.