Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
Veracode
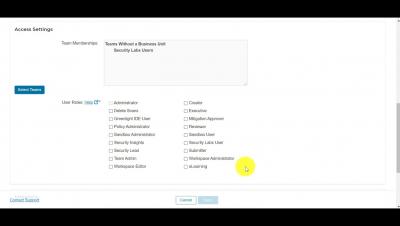
Create Security Labs Users from the Veracode Platform
Executive Order on Cybersecurity Is Imminent: It's Been a Long Time Coming
Following President Biden’s address to Congress last night in which he referenced cybersecurity as a priority twice, news is circulating today that the executive order on cybersecurity is imminent. This news comes as a much awaited and long overdue step towards creating standardization and structure around cybersecurity.
Developer Training Checklist: 5 Best Practices
The role of the developer has evolved over the past several years. Developers are not only responsible for writing code and releasing new software rapidly but also for securing code. By implementing security in the software development lifecycle, you can reduce risk and cost without slowing down time to production. But the developer role is already stretched so thin and many developers don’t have a background in security.
How a Microsoft Engineer Implemented Veracode for a Large Azure Project
With the need to produce innovative software faster than ever, and cyberattacks not slowing down, it’s no surprise that, for projects large and small, ensuring the security of your code at every step is key. But if software engineers want to meet these everyday demands with success, it’s important to understand how different security scanning types fit in throughout the development process, and how the needs of your team might impact scans.
Practical Steps for Fixing Flaws and Creating Fewer Vulnerabilities
All security flaws should be fixed, right? In an ideal world, yes, all security flaws should be fixed as soon as they’re discovered. But for most organizations, fixing all security flaws isn’t feasible. A practical step your organization can – and should – take is to prioritize which flaws should be fixed first.
Reporting Live From Collision Conference 2021: Part Two!
If you caught part one of our recap series on this year’s Collision conference, you know we covered a roundtable talk hosted by Veracode’s own Chris Wysopal. The talk focused on the risks of AI and machine learning, delving into discussions of how to manage the security aspects of these future-ready technologies — especially when it comes down to consumer privacy.
Are You Targeting These Risky Red Zone Vulnerabilities?
Modern software development is full of security risk. Factors like lingering security debt, insecure open source libraries, and irregular scanning cadences can all impact how many flaws dawdle in your code, leading to higher rates of dangerous bugs in susceptible and popular languages.
Reporting Live From Collision Conference 2021: Part One!
This week, Collision (virtually) kicked off its annual conference, bringing together creatives, builders, influencers, innovators, and other great minds to cover some of the hottest topics in business and technology. Known as ‘America’s fastest-growing tech conference,’ this year Collision featured over 450 speakers with more than 100 hours of content to consume across the three-day event.