Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
Latest News
What is a Zero-Day (0-Day)?
In the world of cybersecurity, zero-day vulnerabilities, zero-day attacks, and zero-day exploits keep many CISOs up at night. These terms, often shrouded in mystery and intrigue, denote a significant risk to digital systems and the sensitive data they hold. Understanding the intricacies of zero-day vulnerabilities and the exploits that leverage them is crucial for individuals, organizations, and governments seeking to fortify their defenses against cyber threats.
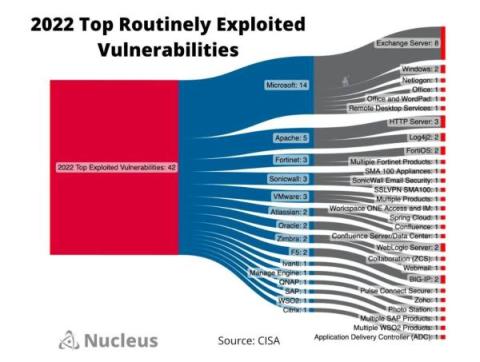
A Look at CISA's Top Routinely Exploited Vulnerabilities
The Latest Trends in API Security: The 2023 OWASP API Security Top Ten
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) has published the latest edition of its API Security Top Ten, which was first published in 2019. The Top Ten is a significant daughter list of the OWASP Top Ten, which is one of the most definitive lists of the most severe web application risks. Why is this important? What are its main findings? And what does this mean for application security?
CVE-2023-38545 & CVE-2023-38546 Curl and libcurl Vulnerabilities: All you need to know
On Wednesday, October 4th 2023, Daniel Stenberg, one of Curl’s core maintainers announced that a forthcoming release of Curl, version 8.4.0, is scheduled to be available on October 11th 2023 at approximately 06:00 UTC. The upcoming release will include fixes for two Curl vulnerabilities that they had discovered. One of these vulnerabilities is rated as having low severity (CVE-2023-38546), whereas the second one is considered high severity (CVE-2023-38545).
Addressing the high severity vulnerability in curl
On October 4, 2023, the curl project maintainers sent out a pre-notification that curl version 8.4.0, expected to be released on October 11 (around 06:00 UTC), will address what they denote as the most serious vulnerability in recent years. Curl is a de-facto standard in the software business when it comes to web requests, and supports a wide range of communication protocols. Depending on the vulnerability, it could have far reaching implications.
Cybersecurity Venture's 2023 Software Supply Chain Attack Report
Most enterprises' critical infrastructure and operational pipelines rely on an intricate web of software, online services, and cloud applications. This level of complexity makes supply chain risk management one of (if not the) biggest challenges for CISOs today. Today, malicious actors choose to exploit software supply chain vulnerabilities rather than just target end users. These SSC attacks have caused some of the most notable cybersecurity incidents and data breaches in recent years.
HTTP/2 Zero-Day Vulnerability Results in Record-Breaking DDoS Attacks
Earlier today, Cloudflare, along with Google and Amazon AWS, disclosed the existence of a novel zero-day vulnerability dubbed the “HTTP/2 Rapid Reset” attack. This attack exploits a weakness in the HTTP/2 protocol to generate enormous, hyper-volumetric Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
SAS and Snyk discuss the future of AI for development and security teams
Composing song lyrics, writing code, securing networks — sometimes it seems like AI can do it all. And with the rise of LLM-based engines like ChatGPT and Google Bard, what once seemed like science fiction is now accessible to anyone with an internet connection. These AI advancements are top-of-mind for most businesses and bring up a lot of questions.