Security | Threat Detection | Cyberattacks | DevSecOps | Compliance
Compliance
Pillars of Amazon Web Services: Security, Identity, and Compliance
As more and more businesses adopt cloud computing services for their operations, the threat against cloud infrastructure is also increasing. AWS, the huge cloud service provider in the market, provides many security features to secure the cloud structure and customer data. It is essential to understand the service provider’s security policy before adopting it for the business.
CMMC 2.0: key changes
Since my previous blog CMMC Readiness was published in September 2021, the Department of Defense (DoD) has made modifications to the program structure and requirements of the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) interim rule first published in September 2020. CMMC 2.0 was officially introduced in November 2021 with the goal of streamlining and improving CMMC implementation.
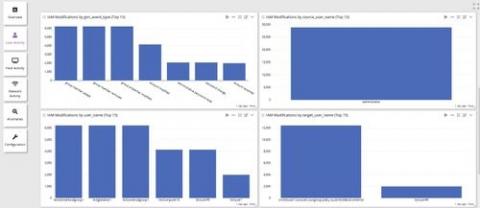
Centralized Log Management for Security and Compliance
#BigPictureCyber Town Hall With Bob Kolasky of Exiger | 5/18/22 | NeoSystems
#BigPictureCyber Town Hall With Stacy Bostjanick, Office of the DoD CIO | 6/1/22 | NeoSystems
May Product Rollup: UI Redesign, Compliance Controls, and More
This month, Egnyte is excited to introduce the start of a redesign to its UI, productivity improvements around shortcuts and the API, new offerings for Advanced Privacy & Compliance and CMMC, continued improvements in governance, and a whole host of new features around course management in the Quality Document Management module for Life Sciences.
CMMC & FedRAMP: FIPS Certified vs. Compliant vs. Validated
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-3 (2019) is “applicable to all federal agencies that use cryptographic-based security systems… and shall be used in designing and implementing cryptographic modules that federal departments and agencies operate or are operated for them under contract.” In other words, any organization that stores, processes, or transmits certain government information must do so in a way that conforms to the FIPS standard.
Protect CUI, FCI for Your Company's CMMC Compliance
If your company does any business with the U.S. Department of Defense, you will be required to comply with CMMC 2.0 to be considered for future contracts. It doesn’t matter if you sell a product or a service, if DoD business is only a small part of your revenue, or if you are only a subcontractor. You will still be required to comply, even if the work you do hasn’t changed. Your business needs to start building a roadmap for CMMC Level 1 or Level 2 compliance.
Top Challenges Faced in the Current Cyber Security Industry
Protecting devices, data, or systems from cyber threats is what cyber security is all about. These cyber-attacks are usually aimed at gaining access to, destroying, or stealing sensitive data, or consumers’ money and disrupting online transactions and business operations. Implementing an effective cyber security system is critical, as the task has grown increasingly difficult.